The Relationship between Health Literacy and Rabies Prevention Behavior of People in Hua Sai District, Nakhon Si Thammarat Province
Keywords:
Health literacy, Disease prevention behaviors, RabiesAbstract
This cross-sectional exploratory study investigated three key aspects of rabies prevention in Hua Sai District, Nakhon Si Thammarat Province: 1) health literacy regarding rabies, 2) rabies prevention behaviors, and 3) the relationship between health literacy and rabies prevention behaviors. A sample of 166 individuals was selected through stratified random sampling, and data were collected using a questionnaire with a reliability coefficient of 0.948. Descriptive statistics and the Spearman rank correlation coefficient were used for data analysis. The findings indicated a high level of health literacy across all areas. The highest average score was in decision-making skills related to rabies (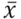 = 4.15, S.D. = 0.52), followed by knowledge and understanding of rabies
= 4.15, S.D. = 0.52), followed by knowledge and understanding of rabies
(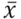 = 4.04, S.D. = 0.52), self-management (
= 4.04, S.D. = 0.52), self-management (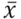 = 4.02, S.D. = 0.57), access to information (
= 4.02, S.D. = 0.57), access to information (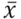 = 3.87, S.D. = 0.53), media literacy (
= 3.87, S.D. = 0.53), media literacy (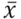 = 3.86, S.D. = 0.56), and communication skills (
= 3.86, S.D. = 0.56), and communication skills (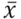 = 3.67, S.D. = 0.58). Rabies prevention behaviors also scored high (
= 3.67, S.D. = 0.58). Rabies prevention behaviors also scored high (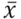 = 3.85, S.D. = 0.52). In terms of correlation, media literacy, self-management, decision-making, knowledge, and communication skills showed moderate correlations with prevention behaviors (r = 0.54, 0.51, 0.49, 0.45, and 0.41, respectively), while access to information showed a low correlation (r = 0.36). Therefore, the Hua Sai District Public Health Office should disseminate information to the public to raise awareness about rabies, promote understanding of the disease, and encourage preventive behaviors to reduce the incidence of illness and fatalities caused by rabies.
= 3.85, S.D. = 0.52). In terms of correlation, media literacy, self-management, decision-making, knowledge, and communication skills showed moderate correlations with prevention behaviors (r = 0.54, 0.51, 0.49, 0.45, and 0.41, respectively), while access to information showed a low correlation (r = 0.36). Therefore, the Hua Sai District Public Health Office should disseminate information to the public to raise awareness about rabies, promote understanding of the disease, and encourage preventive behaviors to reduce the incidence of illness and fatalities caused by rabies.
Downloads
References
สำนักโรคติดต่อทั่วไป กรมควบคุมโรค. ชุดความรู้โรคพิษสุนัขบ้า. พิมพ์ครั้งที่ 3. นนทบุรี, กระทรวงสาธารณสุข. 2554.
World Health Organization. Epidemiology and burden of disease. Switzerland. 2018.
กรมควบคุมโรค. แผนยุทธศาสตร์การกำจัดโรคพิษสุนัขบ้าให้หมดไปภายใน พ.ศ. 2563 (ค.ศ. 2020). กรุงเทพมหานคร, โรงพิมพ์ชุมชนสหกรณ์การเกษตรแห่งประเทศไทย. 2562.
กระทรวงสาธารณสุข. สถานการณ์โรคพิษสุนัขบ้า. นนทบุรี, กระทรวงสาธารณสุข. 2565.
สำนักงานสาธารณสุขจังหวัดนครศรีธรรมราช. รายงานโรคพิษสุนัขบ้า. นนทบุรี, กระทรวงสาธารณสุข. 2567.
กองสุขศึกษา กรมสนับสนุนบริการสุขภาพ. คู่มือนักปรับเปลี่ยนพฤติกรรมสุขภาพ: การพัฒนาความรอบรู้ด้านสุขภาพและการปรับเปลี่ยนพฤติกรรมสุขภาพ. กรุงเทพมหานคร, ชุมนุมสหกรณ์การเกษตรแห่งประเทศไทย จำกัด. 2557.
นิทรา กิจธีระวุฒิวงษ์. การนำความฉลาดทางสุขภาพไปปฏิบัติงานสาธารณสุข. วารสารวิจัยคณะสาธารณสุขศาสตร์ มหาวิทยาลัยขอนแก่น. 2558; 8(2): 68-75.
Parker RM, Baker DW, William MV, and Nurss JR. The test of functional health literacy in adult: A new instrument for measuring patient’s literacy skills. Journal of General International Medicine. 1995; 10: 537-41.
World Health Organization. Health literacy and health promotion, definitions, concepts and examples in the Eastern Mediterranean Region. Accessed 20 January 2024 from https://www.afro.who.int/news/7th-global-conference-health-promotion-president-kibaki-urges-more-resources-african-health.
พุธิตา ภูมี. ปัจจัยที่มีผลต่อพฤติกรรมการป้องกันโรคพิษสุนัขบ้าของเจ้าของสัตว์เลี้ยง ตำบลพุทธบาท อำเภอชนแดน จังหวัดเพชรบูรณ์. [วิทยานิพนธ์]. ปริญญาสาธารณสุขศาสตรมหาบัณฑิต, คณะสาธารณสุขศาสตร์, มหาวิทยาลัยนเรศวร. 2564.
กู้เกียรติ ก้อนแก้ว, วรรณภา เรือนทอง, และอรวรรณ อัตถะบูรณ์. ปัจจัยทำนายพฤติกรรมการป้องกันโรคพิษสุนัขบ้าในเขตอำเภอบางระกำ จังหวัดพิษณุโลก. วารสารวิชาการสาธารณสุข. 2564; 29(4): 601-7.
สำนักงานสาธารณสุขอำเภอหัวไทร. รายงานประจำปี 2566. นครศรีธรรมราช, สำนักงานสาธารณสุขอำเภอหัวไทร. 2566.
Faul F, Erdfelder E, Lang AG, and Buchner A. G*power 3: A flexible statistical power analysis program for the social, behavioral, and biomedical sciences. Behavior Research Methods. 2007; 39(2): 175-91.
Cohen J. Statistical power analysis for the behavioral sciences. 2nd ed. Hillsdale, Lawrence Erlbaum Associates Publishers. 1998.
จันทกานต์ วลัยเสถียร. ความรอบรู้ด้านสุขภาพกับการป้องกันควบคุมโรคพิษสุนัขบ้าแกนนำชุมชนในพื้นที่อำเภอศรีณรงค์ จังหวัดสุรินทร์. [รายงานวิจัย]. สำนักงานป้องกันควบคุมโรคที่ 9 จังหวัดนครราชสีมา. 2564.
Likert R. A technique for the measurement of attitude. Archives of Psychology. 1932; 140: 1-55.
Best JW. Research in education. 3nd ed. Englewood Cliffs, Prentice-Hall. 1977.
Bartz AE. Basic statistical concepts. 4th ed. New Jersey, Prentice–Hall. 1999.
นภดล จันทร์เอี่ยม, ณัฐณีย์ มีมนต์, และภัทรียา กิจเจริญ. ปัจจัยกำหนดความรอบรู้ด้านสุขภาพและพฤติกรรมที่เกี่ยวข้องกับโรคพิษสุนัขบ้าในนักเรียนระดับมัธยมศึกษาในพื้นที่ประจำถิ่นของโรคพิษสุนัขบ้า. วารสารวิชาการสาธารณสุข. 2565; 31(3): 426-36.
ปานแก้ว รัตนศิลป์กัลชาญ, และกาญจนา เหลืองอุบล. ความรอบรู้ด้านสุขภาพในการป้องกันควบคุมโรคพิษสุนัขบ้าของแกนนำชุมชนพื้นที่ปลอดโรคพิษสุนัขบ้าและพื้นที่ไม่ปลอดภัยโรคพิษสุนัขบ้า เขตสาธารณสุขที่ 7. วารสารศูนย์อนามัยที่ 7 ขอนแก่น. 2565; 14(1): 1-28.
ศิรินันท์ คำสี. ความเชื่อด้านสุขภาพที่ส่งผลต่อพฤติกรรมการป้องกันโรคพิษสุนัขบ้าในพื้นที่มีการระบาด ตำบลหัวไทร อำเภอบางคล้า จังหวัดฉะเชิงเทรา. วารสารกรมการแพทย์. 2561; 43(2): 137-40.
วรรณวิมล สุรินทร์ศักดิ์, กาญจนา อ่ำอินทร์, ประวิทย์ คํานึง, และเอกรินทร์ วัฒนพลาชัยกูร. พฤติกรรมการป้องกันโรคพิษสุนัขบ้าของประชาชนในพื้นที่ชายแดน จังหวัดสระบุรี. วารสารรายงานการเฝ้าระวังทางระบาดวิทยาประจำสัปดาห์ (WESR). 2559; 47(34): 529-35.
Nutbeam D. Health promotion glossary. Health Promotion International. 1998; 13: 349-64.
Nutbeam D. The evolving concept of health literacy. Social Science and Medicine. 2008; 67(12): 2072-78.
Downloads
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
Categories
License
Copyright (c) 2024 Journal of Education and Research in Public Health

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.







