การวิเคราะห์โมเดลโค้งพัฒนาการการให้เหตุผลเชิงจริยธรรมของนักเรียนที่มีต่อการประยุกต์ใช้เทคโนโลยีชีวภาพสมัยใหม่
คำสำคัญ:
การประยุกต์ใช้เทคโนโลยีชีวภาพสมัยใหม่, โมเดลโค้งพัฒนาการ, การให้เหตุผลเชิงจริยธรรมบทคัดย่อ
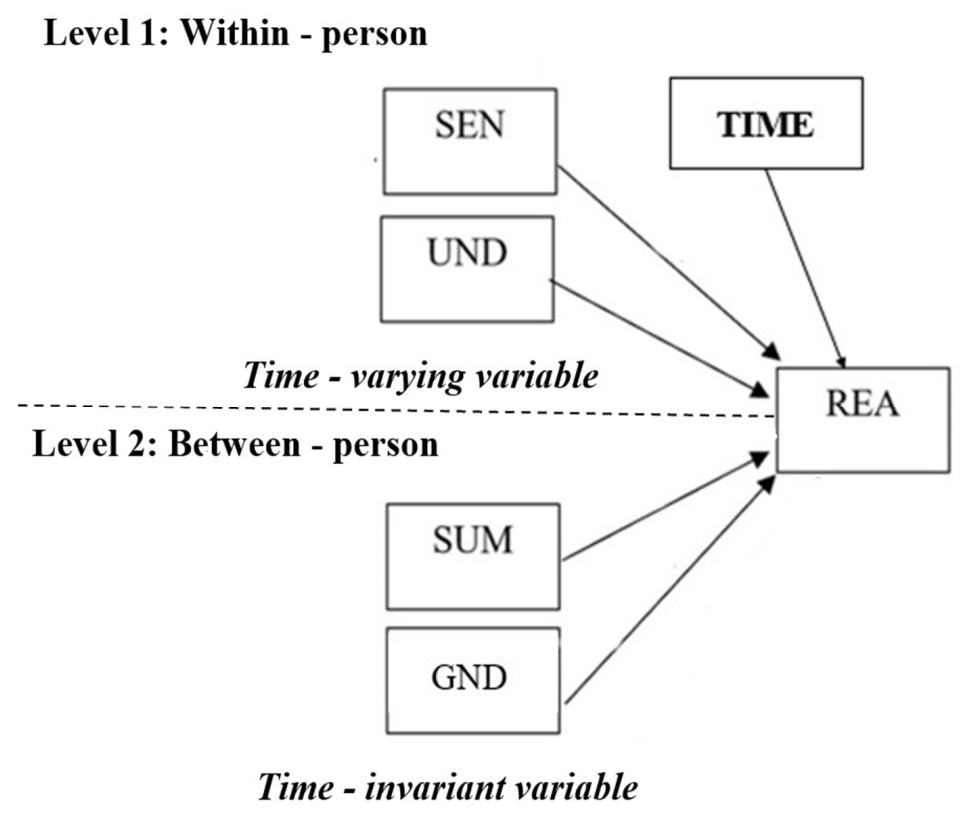
งานวิจัยนี้ศึกษาการเติบโตของการให้เหตุผลเชิงคุณธรรมในนักเรียนเกี่ยวกับประเด็นการประยุกต์ใช้เทคโนโลยีชีวภาพสมัยใหม่ นักเรียนระดับมัธยมปลายจำนวน 206 คนเข้าร่วมในงานวิจัยนี้ นักเรียนถูกวัดการให้เหตุผลเชิงคุณธรรมจำนวน 4 ครั้งใน 1 ภาคการศึกษา ผู้วิจัยตรวจสอบความตรงโมเดลสมมติฐานซึ่งเป็นข้อมูลระยะยาวโดยใช้การวิเคราะห์พหุระดับ วิเคราะห์ข้อมูลด้วยโปรแกรม Mplus 8.0 ผลการวิจัยระบุว่า ร้อยละ 32.6% ของความแปรปรวนมาจากความแตกต่างระหว่างบุคคล (Intraclass coefficient = .326) คะแนนเริ่มต้นของการให้เหตุผลเชิงคุณธรรมมีความแปรปรวน (σ2µ0 = 2.719, p < .001) ความแปรปรวนของคะแนนการให้เหตุผลเชิงคุณธรรมภายในตนเองสามารถอธิบายได้ด้วยเวลาและความอ่อนไหวเชิงคุณธรรม คะแนนการให้เหตุผลเชิงคุณธรรมจะเพิ่มขึ้น 0.19 หน่วย ในการวัดครั้งต่อไป (p < .05) เมื่อพิจารณาความแปรปรวนระหว่างบุคคล ค่าเฉลี่ยคะแนนการให้เหตุผลเชิงคุณธรรมเริ่มต้นมีค่าเท่ากับ 11.33 หน่วย (p < .01) และที่คะแนนเริ่มต้นพบว่า นักเรียนหญิงมีคะแนนสูงกว่า นักเรียนชาย 1.377 หน่วย ความรู้ในเนื้อหาเทคโนโลยีดีเอ็นเอและผลสัมฤทธิ์ทางการเรียนวิชาชีววิทยาก่อนหน้าพบว่า ไม่สามารถอธิบายความแปรปรวนภายในและระหว่างบุคคลได้ตามลำดับ งานวิจัยนี้ได้ให้ข้อเสนอแนะการจัดการศึกษาเพื่อส่งเสริมคุณธรรม
เอกสารอ้างอิง
American Association for the Advancement of Science (AAAS). (1990). Science for All Americans. Oxford University Press.
Andrew, J., & Robottom, I. (2001). Science and ethics: Some issues for education. Science Education, 85, 769–780. https://doi.org/10.1002/sce.1038
Bryk, D.T., & Raudenbush, S. W. (1992). Hierarchical linear model: Applications and data analysis methods. Sage.
Clarkeburn, H. (2002). A test for ethical sensitivity in science. Journal of Moral Education, 31(4), 439–453. https://doi.org/10.1080/0305724022000029662
Črne-Hladnik, H., A. Hladnik, B. Javornik, K. Košmelj and C. Peklaj. (2012). Is judgment of biotechnological ethical aspects related to high school students' knowledge? International Journal of Science Education, 34(8), 1277–1296.
https://doi.org/10.1080/09500693.2011.572264
Dawson, L. M. (1992). Will feminization change the ethics of the sales profession? Journal of Personal Selling and Sales Management, 21–32.
https://www.jstor.org/stable/40471451
Dawson, V. M. & Taylor, P.C. (1999). Teaching bioethics in science: Does it make a difference? Australian Science Teachers’ Journal, 45, 59–64.
Dawson, V. M., & Schibeci R. A. (2003). West Australian school students’ understanding of Biotechnology. International Journal of Science Education, 25, 57–69. https://doi.org/10.1080/09500690210126720
Evans, J. H. (2002). Playing God?: Human genetic engineering and the rationalization of public bioethical debate. University of Chicago Press.
Fowler, S. R., Zeidler, D. L., & Sadler, T. D. (2009). Moral sensitivity in the context of socioscientific issues in high school science students. International Journal of Science Education, 31(2), 279–296.
https://doi.org/10.1080/09500690701787909
Gilligan, C. (1993). In a different voice: Psychological theory and women’s development. Harvard University Press.
Grace, M. M., & Ratcliffe, M. (2002). The science and values that young people draw upon to make decisions about biological conservation issues. International Journal of Science Education, 24, 1157–1169.
https://doi.org/10.1080/09500690210134848
Hair, J. F., Hult, G. T. M., Ringle, C. M., & Sarstedt, M. (2022). A Primer on Partial Least Squares Structural Equation Modeling (PLS-SEM) (3rd ed.). Sage.
Hart, D. (2005). The Development of Moral Identity. In G. Carlo & C. P. Edwards (Eds.), Moral motivation through the life span (pp. 165–196). University of Nebraska Press.
Hox, J. (2010). Multilevel analysis: Techniques and applications. Routledge.
Kohlberg, L. (1969). Stage and sequence: The cognitive developmental approach to socialization. In D. Goslin (Ed.), Handbook of socialization theory and research (pp. 347–480). Rand McNally.
McCoach, D. B., & Kaniskan B. (2010). Using time-varying covariates in multilevel growth models. Frontiers in Psychology, 1, 1–12.
https://doi.org/10.3389/fpsyg.2010.00017
National Research Council of Thailand. (2013). Teachers and strengthening ethics to students. Bangkok. [in Thai]
Olsher, G., & Dreyful, A. (1999). The ‘ostension-teaching approach as a means to develop junior-high student attitudes towards biotechnologies. Journal of Biological Education, 34, 24–30.
https://doi.org/10.1080/00219266.1999.9655679
Pedretti, E. (1999). Decision making and STS education: Exploring science knowledge and social responsibility in schools and science centers through an issues-based approach. School Science and Mathematics, 99, 174–181.
https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1949-8594.1999.tb17471.x
Piaget, J. (1932). The moral judgment of the child. Harcourt, Brace.
Raudenbush, S. W., & Bryk, A. S. (2002). Hierarchical linear models: Application and data analysis methods (2nd ed.). Sage.
Rest, J. R. (1986). Moral development: Advances in research and theory. Praeger.
Sadler, T. D., & Zeidler, D. L. (2005a). Patterns of informal reasoning in the context of socio-scientific decision-making. Journal of Research in Science Teaching, 42(1), 112–138. https://doi.org/10.1002/tea.20042
Sadler, T. D., & Zeidler, D. L. (2005b). The significant of content knowledge for informal reasoning regarding socioscientific issues: Applying genetics knowledge to genetic engineering issues. Science Education, 89(1), 71–93.
https://doi.org/10.1002/sce.20023
Singer, J. D., & Willet, J. B. (2003). Applied longitudinal data analysis. Oxford University Press.
Stock, G., & Campbell, J. (2000). Engineering the human germline: An exploration of the science and ethics of altering the genes we pass to our children. Oxford University Press.
Zeidler. D. L. (1984). Moral issues and social policy in science education: Closing the literacy gap. Science Education, 68, 411–419.
https://doi.org/10.1002/sce.3730680406
Zohar, A., & Nemet, F. (2002). Fostering students’ knowledge and argumentation skills through dilemmas in human genetics. Journal of Research in Science Teaching, 39, 35–6. https://doi.org/10.1002/tea.10008
ดาวน์โหลด
เผยแพร่แล้ว
รูปแบบการอ้างอิง
ฉบับ
ประเภทบทความ
สัญญาอนุญาต
ลิขสิทธิ์ (c) 2024 ภาควิชาวิจัยและจิตวิทยาการศึกษา คณะครุศาสตร์ จุฬาลงกรณ์มหาวิทยาลัย

อนุญาตภายใต้เงื่อนไข Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.
บทความที่ตีพิมพ์ในวารสารนี้อยู่ภายใต้สัญญาอนุญาต Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International (CC BY-NC-ND 4.0)


