The Development and Validation of a Model of the Intention to Adopt and Integrate ICT into Science Teaching
Keywords:
Structural Equation Modeling, Adoption and Integration of ICT into Science Teaching, Science TeachersAbstract
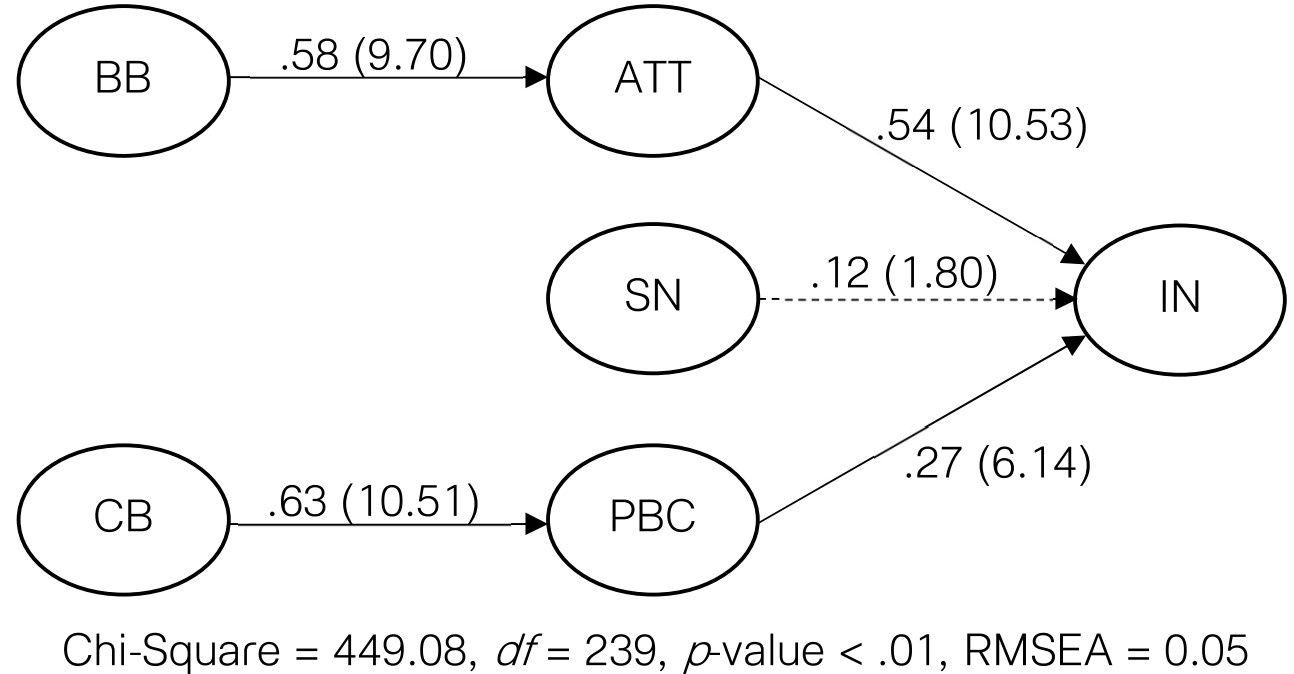
This study aims to develop and test a causal model of teachers’ intention to adopt and integrate ICT into teaching science, guided by Ajzen’s Theory of Planned Behavior. The data were retrieved from the International Association for the Evaluation of Educational Achievement (IEA)’s database on the Second Information Technology in Education Study (SITES) 2006. The sample comprised 679 science teachers from 465 schools in 13 educational service areas in Thailand. To empirically test the model, LISREL 9.1 was employed. The results indicate that the model for ordinal variables provided an acceptable fit to the data (χ2 = 449.08, df = 239; χ2/df = 1.87, p < .01, RMSEA = 0.05, CFI = .99). Attitude (β = .54, p < .01) and perceived behavioral control (β = .27, p < .01) were significantly related to intention. However, the relationship between subjective norm and intention was not significant
(β = .12, p > .05). These three determinants collectively explained 52% of the variance in intention.
References
Admiraal, W., van Vugt, F., Kranenburg, F., Köster, B., Smit, B., Weijers, S., & Lockhorst, D. (2016). Preparing pre-service teachers to integrate technology into K–12 instruction: Evaluation of a technology-infused approach. Technology, Pedagogy and Education, 26(1), 105–120. https://doi.org/10.1080/1475939x. 2016.1163283
Ajzen, I. (1985). From intentions to actions: A theory of planned behavior. In J. Kuhi & J. Beckmann (Eds.) Actionócontrol: From cognition to behavior, (11-39). Springer.
Ajzen, I., & Fishbein, M. (1980). Understanding attitudes and predicting social behavior. Prentice Hall.
Anderson, J. C., & Gerbing, D. W. (1988). Structural equation modeling in practice: A review and recommended two-step approach. Psychological Bulletin, 103(3), 411- 423.
Armitage, C. J., & Conner, M. (2001). Efficacy of the theory of planned behaviour: A meta- analytic review. British Journal of Social Psychology, 40, 471–499.
ASEAN (2011). Master plan on ASEAN connectivity: One vision, one identity, one community. Retrieved from http://www.aseansec.org/documents/MPAC.pdf.
Becker, H. J. (2001, April). How are teachers using computers in instruction? Paper presented at the Annual Meeting of the American Educational Researcher Association, Seattle.
Bahçıvan, E., Gürer, M. D., Yavuzalp, N., & Akayoğlu, S. (2019). Investigating the Relations Among Pre-Service Teachers’ Teaching/Learning Beliefs and Educational Technology Integration Competencies: a Structural Equation Modeling Study. Journal of Science Education and Technology, 28(5), 579–588. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10956-019-09788-6
Cuban, L. (1999). The technology puzzle: Why is greater access not translating into better classroom use? Education Week, 4, 68.
Demirci, A. (2009). How do teachers approach new technologies: Geography teachers’ attitudes towards Geographic Information Systems (GIS). European Journal of Educational Studies, 1(1), 43-53.
Drent, M., & Meelissen, M. (2008). Which factors obstruct or stimulate teacher educators to use ICT innovatively? Computers & Education, 51(1), 187-199.
Finnay, S. J., & DiStefano, C. (2006). Non-normal and categorical data in structural equation modeling. In G.R. Hancock & R. O. Mueller (Eds.), Structural equation modeling: A second course. Information Age Publishing.
Goldstein, G. (1997). Information technology in English schools: A commentary on inspection findings 1995-6. Coventry: NCET/OFSTED.
Hansen, T., & Jensen, J.M. (2007). Understanding consumers’ political voting decisions: A Theory of Planned Behavior Approach. Innovative Marketing, 3(4), 86-93.
Hou, M. Lin, Y. , Shen, Y., & Zhou. (2022). Explaining pre-service teachers’ intentions to use technology-enabled learning: An extended model of the Theory of Planned Behavior. Frontier in Psychology, 13, 1-13.
Kijtorntham, W., Andhivarothai, P., Kaewkor, S., & Yamtim, W. (2012). Scenarios of Thai pre-service teacher education in the next 20 years: Applying of futures wheel technique. Journal of Research Methodology, 25(3), 275-294.
Law, N., Pelgrum, W.J., & Plomp, T. (Eds.). (2008). Pedagogy and ICT use in schools around the world: Findings from the IEA SITES 2006 study. CERC- Springer.
Marcinkiewicz, H. (1996). Motivation and teachers' computer use. Paper presented at the Proceedings of selected research and development presentations at the 1996 National Convention of the Association for Educational Communications and Technology, ED 397 818.
Ministry of Information and Communication Technology (MICT). (2011). Executive summary of the Thailand ICT Policy Framework: 2011-2020 (ICT 2020). Retrieved from http://www.ict2020.in.th
Osborne, J., & Hennessy, S. (2003). Literature review in Science and the role of ICT: Promise, problems, and future directions. Futurelab Series
Peralta, H., & Costa, F.A. (2007). Teachers’ competence and confidence regarding the use of ICT. Educational Sciences Journal, 3, 75-84.
Plomp, T., Anderson, R. E., Law, N., & Quale, A. (2009). Cross-national information and communication technology: Policies and practices in education (2nd ed.). Information Age Publishing.
Preston, C., Cox, M. J., & Cox, K. (2000). Teachers as innovators: An evaluation of the motivation of teachers to use information and communications technologies. Mirandanet.
Sutton, S. (1998). Predicting and explaining intentions and behavior: How well are we doing? Journal of Applied Social Psychology, 28(15), 1317-1338.
Veen, V. (1993). The role of beliefs in the use of information technology: implications for teacher education or teaching the right thing at the right time. Journal of Information Technology for teacher education, 2(2), 139-153.
Williams, D., Coles, L., Wilson, K., Richardson, A., & Tuson, J. (2000). Teachers and ICT: current use and future needs. British Journal of Educational Technology, 31(4), 307-320.
Yang-Wallentin, F., Jöreskog, K. G., & Luo, H. (2010). Confirmatory factor analysis of ordinal variables with misspecified models. Structural Equation Modeling: A Multidisciplinary Journal, 17(3), 392-423.
Yu, C.Y. (2002). Evaluating cutoff criteria of model fit indices for latent variable models with binary and continuous outcomes (Unpublished doctoral dissertation). University of California, Los Angeles.
Yuen, A. H. K., & Ma, W. W. K. (2008). Exploring teacher acceptance of E-learning technology. Asia-Pacific Journal of Teacher Education, 36(3), 229-243.
Downloads
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2023 Department of Educational Research and Psychology, Faculty of Education, Chulalongkorn University

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.
All published content in JRM is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License (CC BY-NC-ND 4.0).


