Determining the Appropriate Sample Size in EFL Pilot Studies
Keywords:
Pilot Studies, Survey Research, EFL, Sample Size, ReliabilityAbstract
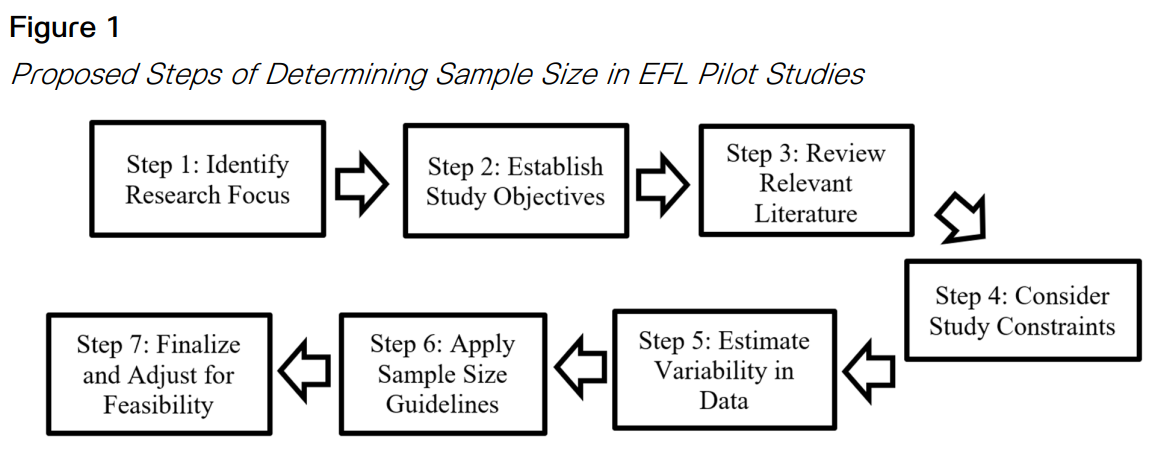
Pilot studies are fundamental in the field of English as a foreign language (EFL) as they provide opportunities to evaluate and improve the research design and instruments. This review summarizes key researchers’ suggestions for determining sample size in EFL pilot studies and offers instructions for conducting pilot studies in this context. For example, a range of 10 to 30 participants is suitable for pilot studies, while 30 participants are generally sufficient for a questionnaire. Additionally, about a dozen subjects in a group are sufficient when estimating distribution parameters. Guidelines for reliability are also formulated. This review therefore enhances EFL research by providing a practical understanding of sample size recommendations and their implications in EFL settings, thereby assisting researchers in designing effective EFL pilot studies. This will increase the credibility and relevance of EFL research and contribute to the development of more comprehensive and trustworthy studies in the future.
References
Andrade, C. (2020). Sample size and its importance in research. Indian Journal of Psychological Medicine, 42(1), 102–103. https://doi.org/10.4103/IJPSYM.IJPSYM_504_19
Azman, N. A., Hamzah, M. I., Abdul Razak, K., & Zulkifli, H. (2024). Digital competence among Islamic teachers: A pilot study on validity and reliability. The Turkish Online Journal of Educational Technology, 23(4), 51-62.
Bachman, L. F., & Palmer, A. S. (1996). Language testing in practice: Designing and developing useful language tests. Oxford University Press.
Brown, H. D. (2014). Principles of language learning and teaching (6th ed.). Longman.
Bujang, M. A., Omar, E. D., & Baharum, N. A. (2018). A review on sample size determination for Cronbach's alpha test: A simple guide for researchers. The Malaysian Journal of Medical Sciences (MJMS), 25(6), 85–99. https://doi.org/10.21315/mjms2018.25.6.9
Bujang, M. A., Omar, E. D., Foo, D. H. P., & Hon, Y. K. (2024). Sample size determination for conducting a pilot study to assess reliability of a questionnaire. Restorative Dentistry & Endodontics, 49(1), 1–8. https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2024.49.e3
Cohen, J., Cohen, P., West, S. G., & Aiken, L. S. (2007). Applied multiple regression/correlation analysis for the behavioral sciences (3rd ed.). Routledge.
Cronbach, L. J. (1951). Coefficient alpha and the internal structure of tests. Psychometrika, 16(3), 297–334. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02310555
DeVellis, R. F. (2012). Scale development: Theory and applications (3rd ed.). Sage Publications.
Elder, C., & O’Loughlin, K. (2003). Investigating the relationship between intensive English language instruction and band score gain on IELTS. IELTS Research Reports, 4, 207–254.
George, D., & Mallery, P. (2003). SPSS for Windows step by step: A simple guide and reference. Allyn & Bacon.
Giner-Sorolla, R., Montoya, A. K., Reifman, A., Carpenter, T., Lewis, N. A., Aberson, C. L., Bostyn, D. H., Conrique, B. G., Ng, B. W., Schoemann, A. M., & Soderberg, C. (2024). Power to detect what? Considerations for planning and evaluating sample size. Personality and Social Psychology Review, 28(3), 276–301. https://doi.org/10.1177/10888683241228328
Hair, J. F., Black, W. C., Babin, B. J., & Anderson, R. E. (2018). Multivariate data analysis (8th ed.). Pearson.
Hertzog, M. A. (2008). Considerations in determining sample size for pilot studies. Research in Nursing & Health, 31(2), 180–191. https://doi.org/10.1002/nur.20247
In, J. (2017). Introduction of a pilot study. Korean Journal of Anesthesiology, 70(6), 601–605. https://doi.org/10.4097/kjae.2017.70.6.601
Johanson, G. A., & Brooks, G. P. (2010). Initial scale development: Sample size for pilot studies. Educational and Psychological Measurement, 70(3), 394–400. https://doi.org/10.1177/0013164409355692
Julious, S. A. (2005). Sample size of 12 per group rule of thumb for a pilot study. Pharmaceutical Statistics, 4(4), 287–291. https://doi.org/10.1002/pst.185
Kraemer, H. C., Mintz, J., Noda, A., Tinklenberg, J., & Yesavage, J. A. (2006). Caution regarding the use of pilot studies to guide power calculations for study proposals. Archives of General Psychiatry, 63(5), 484–489. https://doi.org/10.1001/archpsyc.63.5.484
Kunselman, A. R. (2024). A brief overview of pilot studies and their sample size justification. Fertility and Sterility, 121(6), 899–901. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fertnstert.2024.01.040
Leon, A. C., Davis, L. L., & Kraemer, H. C. (2011). The role and interpretation of pilot studies in clinical research. Journal of Psychiatric Research, 45(5), 626–629. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jpsychires.2010.10.008
McNamara, T. F. (1996). Measuring second language performance. Longman.
Nunnally, J. C. (1978). Psychometric theory (2nd ed.). McGraw-Hill.
OECD. (2019). PISA 2018 results (Volume I): What students know and can do. OECD Publishing. https://doi.org/10.1787/5f07c754-en
Sukserm, P. (2024). Understanding latent variables in EFL contexts. Shanlax International Journal of Education, 12(4), 60–69. https://doi.org/10.34293/education.v12i4.7886
Tabatabaei, O., & Loni, M. (2015). Problems of teaching and learning English in Lorestan province high schools, Iran. Mediterranean Journal of Social Sciences, 6(2 S1), 47–55. https://doi.org/10.5901/mjss.2015.v6n2s1p47
Taber, K. S. (2018). The use of Cronbach’s alpha when developing and reporting research instruments in science education. Research in Science Education, 48(6), 1273–1296. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11165-016-9602-2
Tegeh, I. M., Jampel, I. N., & Pudjawan, K. (2014). The effectiveness of the EFL reading comprehension test. Journal of Educational Research and Evaluation, 3(1), 12–22.
Teresi, J. A., Yu, X., Stewart, A. L., & Hays, R. D. (2022). Guidelines for designing and evaluating feasibility pilot studies. Medical Care, 60(1), 95–103. https://doi.org/10.1097/MLR.0000000000001664
Thabane, L., Ma, J., Chu, R., Cheng, J., Ismaila, A., Rios, L. P., et al. (2010). A tutorial on pilot studies: What, why and how. BMC Medical Research Methodology, 10(1), 1–10. https://doi.org/10.1186/1471-2288-10-1
Van Teijlingen, E., & Hundley, V. (2001). The importance of pilot studies. Social Research Update, 35, 1–4.
Vo, T. K. A., Long, N. V., & Vo, H. T. T. N. (2024). EFL learners’ readiness and challenges for immediate online learning: A case study in Vietnam. Journal of Institutional Research South East Asia, 22(2), 141–158.
Downloads
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2024 Patsawut Sukserm

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.
All published content in JRM is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License (CC BY-NC-ND 4.0).


