Factors Influencing Responsible Behavior and Destination Choice of Visitors: A Case Study of Chiang Khan Community, Loei Province
Keywords:
Responsible Tourism, Responsible Behavior, Choice of DestinationAbstract
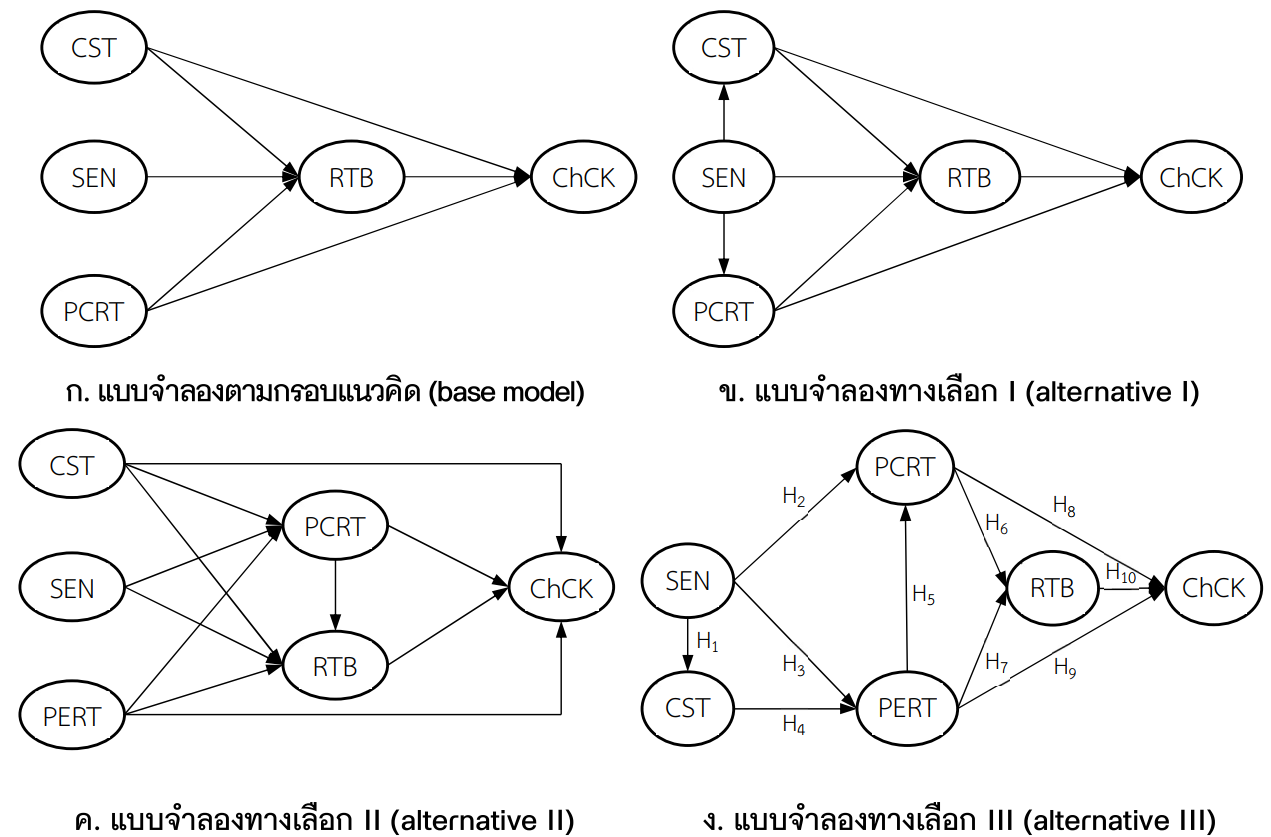
This study aims to investigate the causal relationship between factors influencing Thai visitors’ responsible behavior and their choice of Chiang Khan as a tourism destination. The model consists of six latent variables measured from 20 observational variables. The sample comprised 298 Thai visitors who visited Chiang Khan, located in Loei province. Questionnaires were utilized as the research tool, while structural equation modeling was applied to analyze the data. The results indicate that focusing on social participation and increasing awareness of responsible tourism management are two key factors influencing visitors’ responsible behavior and their choice of Chiang Khan as a tourist destination. Therefore, to encourage responsible behavior among visitors and promote Chiang Khan as a tourism destination, relevant sectors should develop and disseminate information on responsible tourism stewardship and management through various channels, such as video clips, online and social media platforms, influencers, etc., to effectively communicate with visitors and interested parties.
References
กระทรวงการท่องเที่ยวและกีฬา. (2564). แผนพัฒนาการท่องเที่ยวแห่งชาติ ฉบับที่ 3 พ.ศ. 2566-2570. กระทรวงการท่องเที่ยวและกีฬา.
การท่องเที่ยวแห่งประเทศไทย. (2562). โครงการสำรวจพฤติกรรมการเดินทางท่องเที่ยวของชาวไทย พ.ศ. 2562. รายงานฉบับสมบูรณ์. การท่องเที่ยวแห่งประเทศไทย.
Ballantyne, R., Packer, J., & Falk, J. (2011). Visitors’ learning for environmental sustainability: Testing short- and long-term impacts of wildlife tourism experiences using structural equation modeling. Tourism Management, 32(6), 1243-1252.
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tourman.2010.11.003
Budeanu, A. (2007). Sustainable tourist behaviour -a discussion of opportunities for change. International Journal of Consumer Studies, 31(5), 499-508.
Camilleri, M. A. (2016). Responsible tourism that creates shared value among stakeholders. Tourism Planning Development, 13(2), 219-235. https://doi.org/10.1080/21568316.2015.1074100
Caruana, R., Glozer, S., Crane, A., & McCabe, S. (2014). Tourists’ accounts of responsible tourism. Annals of Tourism Research, 46(May), 115-129. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.annals.2014.03.006
Chiappa, G. D., Grappi, S., & Romani, S. (2016). Attitudes towards responsible tourism and behavioral change to practice it: A demand-side perspective in the context of Italy. Journal of Quality Assurance in Hospitality & Tourism, 7(2), 191-208.
https://doi.org/10.1080/1528008X.2015.1115254
Diallo, M. F., Diop-Sall, F., Leroux, E., & Valette-Florence, P. (2015). Responsible tourist behavior: The role of social engagement. Recherche et Applications en Marketing, 30(3), 85-104.
https://doi.org/10.1177/205157071559413
Frey, N. & George, R. (2010). Responsible tourism management: The missing link between business owners’ attitudes and behaviour in the Cape Town tourism industry. Tourism Management, 31(5), 621-628. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tourman.2009.06.017
Goodwin, H. (2002). The case for responsible tourism. In T. Jenkins (Ed.), Ethical tourism: Who benefits? Hodder and Stoughton.
Goodwin, H. (2011). Taking responsibility for tourism: Responsible tourism management. Goodfellow Publishers Limited.
Hair, J. F., Black, W. C., Babin, B. J., & Anderson, R. E. (2010). Multivariate data analysis (7th ed.). Prentice-Hall International.
Hu, L. T. & Bentler, P. M. (1999). Cutoff criteria for fit indexes in covariance structure analysis: conventional criteria versus new alternatives. Structural Equation Modeling, 6(1), 1-55.
https://doi.org/10.1080/10705519909540118
Jöreskog, K. G. & Sörbom, D. (1999). LISREL 8 user’s reference guide. Scientific Software International.
Kim, M. J., Park, J. Y., Reisinger, Y., & Lee, C. K. (2018). Predicting responsible tourist behavior. International Journal of Tourism and Hospitality Research, 32(4), 5-20.
DOI: 0.21298/IJTHR.2018.4.32.4.5
Kline, R. B. (2012). Assumptions of structural equation modeling. In R. Hoyle (Ed.), Handbook of structural equation modeling. Guilford Press.
Kline, R. B. (2011). Principles and practice of structural equation modeling (3rd ed.). Guilford Press.
Lee, T. H., Jan, F. H., & Yang, C. C. (2013). Conceptualizing and measuring environmentally responsible behaviors from the perspective of community-based tourists. Tourism Management, 36(June), 454-468. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tourman.2012.09.012
Mathew, P. V. & Sreejesh, S. (2017). Impact of responsible tourism on destination sustainability and quality of life of community in tourism destinations. Journal of Hospitality and Tourism Management, 31(June), 83-89. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhtm.2016.10.001
Muthén, L. K. & Muthén, B. O. (2012). Mplus user’s guide (7th ed.). Muthén & Muthén.
Paul, V. M. & Rupesh, K. K. (2014). Responsible tourism: A strategy for grass root level empowerment. Innovative Issues and Approaches in Social Sciences, 7(1), 53-70.
https://doi.org/10.12959/issn.1855-0541.IIASS-2014-no1-art04
Steiger, J. H. (2007). Understanding the limitations of global fit assessment in structural equation modeling. Personality and Individual Differences, 42(5), 893-898.
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.paid.2006.09.017
Stoffelen, A., Adiyia, B., Vanneste, D., & Kotze, N. (2020). Post- apartheid local sustainable development through tourism: an analysis of policy perceptions among ‘responsible’ tourism stakeholders around Pilanesberg National Park, South Africa. Journal of Sustainable Tourism, 28(3), 414-432. https://doi.org/10.1080/09669582.2019.1679821
Tabachnick, B. G. & Fidell, L. S. (2013). Using multivariate statistics (6th ed.).Pearson.
Um, S. & Crompton, J. (1990). Attitude determinants in tourism destination choice. Annals of Tourism Research, 17(3), 432-448. https://doi.org/10.1016/0160-7383(90)90008-F
Yoon, A., Jeong, D., Chon, J., & Yoon, J. -H. (2019). A study of consumers’ intentions to participate in responsible tourism using message framing and appeals. Sustainability, 11(3), 1-14.
https://doi.org/10.3390/su11030865
Zagonari, F. (2019). Multi-criteria, cost-benefit, and life-cycle analyses for decision-making to support responsible, sustainable, and alternative tourism. Sustainability, 11(4), 1-35.
https://doi.org/10.3390/su11041038
Zgolli, S. & Zaiem, I. (2018). The responsible behavior of tourist: The role of personnel factors and public power and effect on the choice of destination. Arab Economics and Business Journal, 13(2), 168-178. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aebj.2018.09.004
Translated Thai References
Ministry of Tourism and Sports. (2021). National Tourism Development Plan No. 3 (2023-2027). Bangkok: Ministry of Tourism and Sports.
Tourism Authority of Thailand. (2019). Travel Behavior Survey Project of Thai People 2019. Final Report. Bangkok: Tourism Authority of Thailand.
Downloads
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2024 The Authors

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.
All published content in JRM is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License (CC BY-NC-ND 4.0).


